World Economic Outlook
World Economic Outlook, April 2020: The Great Lockdown
April 2020
Chapter 1: Global Prospects and Policies
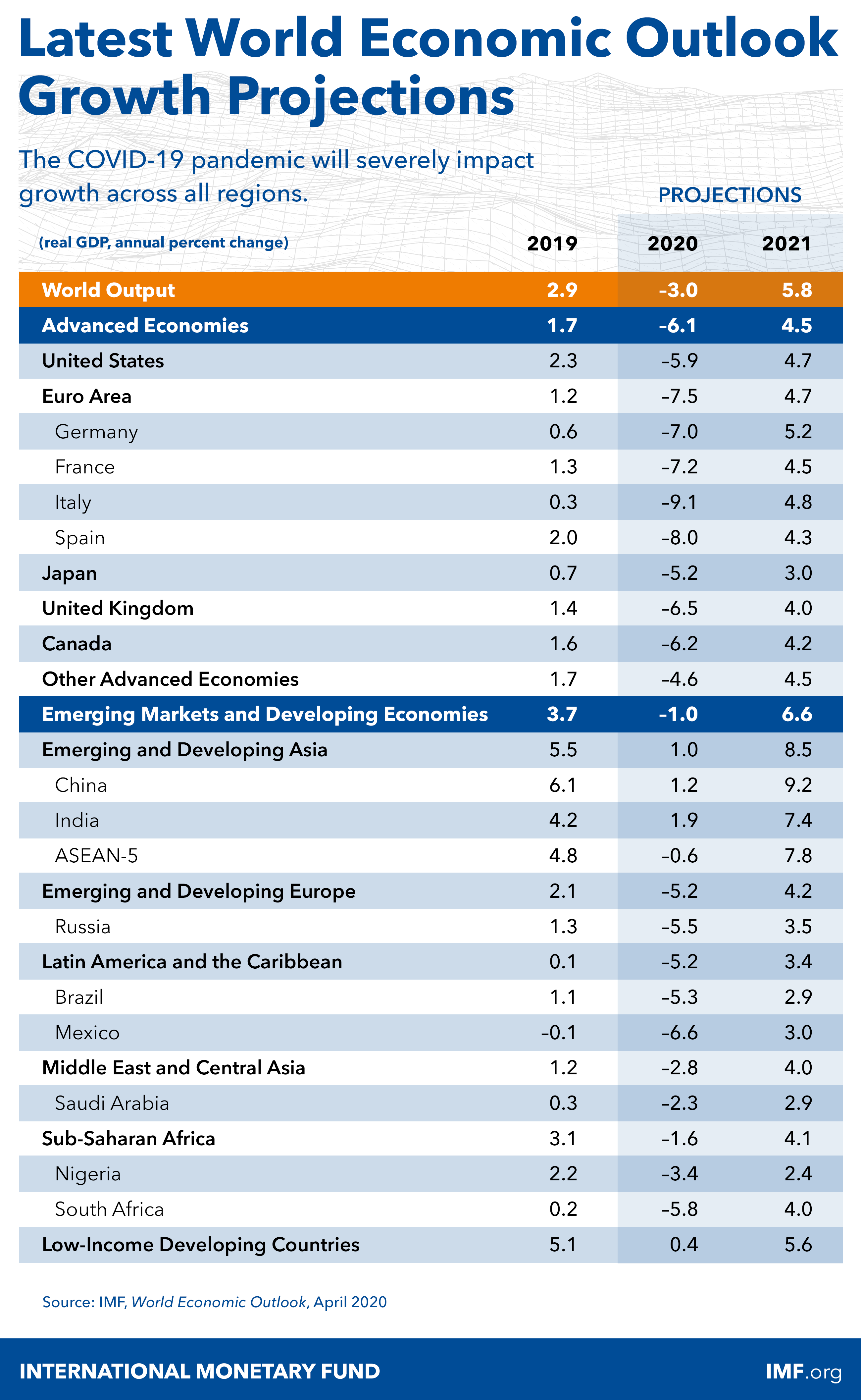
The COVID-19 pandemic is inflicting high and rising human costs worldwide, and the necessary protection measures are severely impacting economic activity. As a result of the pandemic, the global economy is projected to contract sharply by –3 percent in 2020, much worse than during the 2008–09 financial crisis. In a baseline scenario--which assumes that the pandemic fades in the second half of 2020 and containment efforts can be gradually unwound—the global economy is projected to grow by 5.8 percent in 2021 as economic activity normalizes, helped by policy support. The risks for even more severe outcomes, however, are substantial. Effective policies are essential to forestall the possibility of worse outcomes, and the necessary measures to reduce contagion and protect lives are an important investment in long-term human and economic health. Because the economic fallout is acute in specific sectors, policymakers will need to implement substantial targeted fiscal, monetary, and financial market measures to support affected households and businesses domestically. And internationally, strong multilateral cooperation is essential to overcome the effects of the pandemic, including to help financially constrained countries facing twin health and funding shocks, and for channeling aid to countries with weak health care systems.
Chapter 2: Countering Future Recessions in Advanced Economies: Cyclical Policies in an Era of Low Rates and High Debt
More than a decade after the global financial crisis, the world is struggling with the health and economic effects of a profound new crisis caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. Advanced economies entered this crisis with interest rates at historical lows and public debts, on average, higher than they had been over the past 60 years. They will come out from the crisis with even higher public debts. Drawing on analysis completed before the emergence of the pandemic, this chapter examines policymakers’ options to respond to adverse shocks and build resilience when rates are low and debts high.
Chapter 3: Dampening Global Financial Shocks in Emerging Markets: Can Macroprudential Regulation Help?
As discussed in Chapter 1, the COVID-19 pandemic is impacting emerging markets through an unprecedented mix of domestic and external shocks whose combined effects are very hard to predict. Among these, emerging markets are confronting a sharp tightening in global financial conditions. Against this backdrop, this chapter asks whether, based on historical experience, countries that have adopted a more stringent level of macroprudential regulation—aimed at strengthening financial stability—are better placed to withstand the impact of global financial shocks on domestic macroeconomic conditions.
Chapter 4: The Macroeconomic Effects of Global Migration
The share of immigrants in advanced economies has risen significantly in recent years, while escalating conflicts have caused large refugee flows that have primarily affected emerging market and developing economies. This chapter examines the drivers of migration, its recent evolution, its possible developments going forward, and its economic impact on recipient countries.