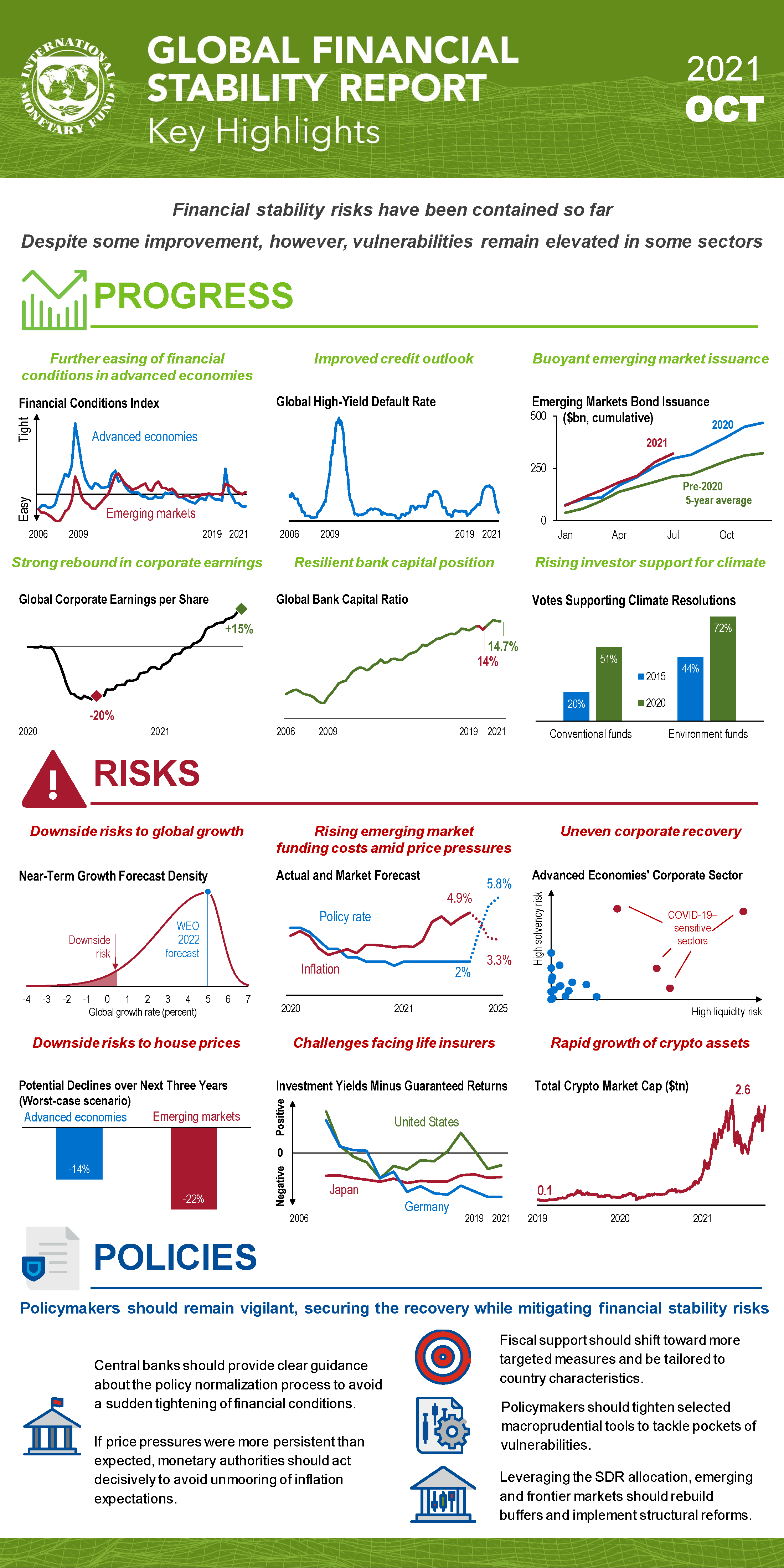
Financial stability risks contained so far, but despite improvements vulnerabilities remain elevated in some sectors

Financial stability risks have been contained so far, reflecting ongoing policy support and a rebound in the global economy earlier this year. Chapter 1 explains that financial conditions have eased further in net in advanced economies but changed little in emerging markets. However, the optimism that propelled markets earlier in the year has faded on growing concerns about the strength of the global recovery, and ongoing supply chain disruptions intensified inflation concerns. Signs of stretched asset valuations in some market segments persist, and pockets of vulnerabilities remain in the nonbank financial sector; recovery is uneven in the corporate sector.
Chapter 2 discusses the opportunities and challenges of the crypto ecosystem. Crypto asset providers’ lack of operational or cyber resilience poses risks, and significant data gaps imperil financial integrity. Crypto assets in emerging markets may accelerate dollarization risks. Chapter 3 shows that sustainable funds can support the global transition to a green economy but must be scaled up to have a major impact. It also discusses how a disorderly transition could disrupt the broader investment fund sector in the future.
Chapter 1: Global Financial Stability Overview: A Delicate Balancing Act
As the world continues to navigate the pandemic, financial stability risks have been contained so far thanks to the ongoing policy support. However, financial vulnerabilities remain elevated in several sectors. Concerns about upside risks to the inflation outlook persist and asset valuations are stretched in some market segments. Emerging and frontier markets continue to face large financing needs amid higher funding costs. Risks are also rising at some nonbank financial institutions as they reach for yield to meet return targets.
Chapter 2: The Crypto Ecosystem and Financial Stability Challenges
The crypto ecosystem offers an exciting new world of opportunities but also challenges. Risks to consumers can arise from a lack of operational or cyber resilience associated with crypto asset providers. Anonymity and limited global standards create significant data gaps for regulators and pose risks to financial integrity. The advent of crypto assets and stablecoins in emerging market and developing economies may accelerate dollarization risks. The chapter concludes with a set of eight actionable policy recommendations.
Chapter 3: Investment Funds: Fostering the Transition to a Green Economy
This chapter analyzes the role that the global investment fund sector can play to support the urgently needed transition to a green economy, as well as the risks to the sector arising from this transition. The chapter’s findings suggest that policymakers should strengthen the global climate information architecture to foster climate finance markets, ensure proper regulatory oversight to prevent greenwashing, and conduct scenario analysis and stress testing to mitigate financial stability risks.
Publications

-
June 2024
Finance & Development
- An IMF for Tomorrow

-
September 2023
Annual Report
- Committed to Collaboration

-
Regional Economic Outlooks
- Latest Issues